Nanofiltration NF Systems
The fundamental principle of Nanofiltration membrane's technology is the use of pressure to separate soluble ions from water through a semi permeable membrane. The membrane, operates under a different hydraulic profile which is also known cross flow filtration, unlike a dead end filter.
Most Nanofiltration membranes are composite materials supported by polymer substrate and manufactured in a spiral design as opposed to a flat sheet or tube geometry. The predominant model used today for industrial applications is the spiral configuration. To ascertain further understanding of nanofiltration systems, you will need to be aware of the following information.
Like RO, and unlike UF, Nanofiltration Systems will recover a percentage of the feed water. Most all NF membranes are of a spiral wound configuration.
Daily Capacity Range:
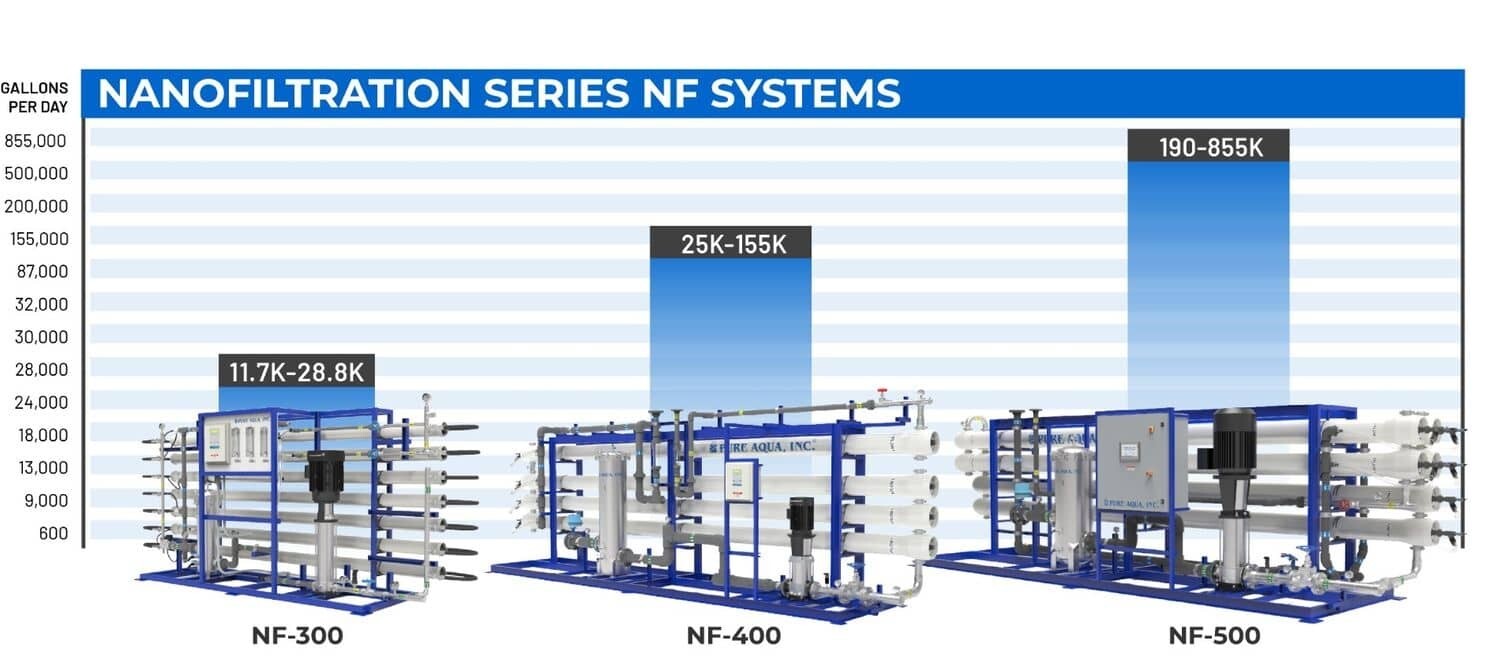
11,700 to 28,800 GPD
(44 to 109 M³/day)
- Membrane Diameter: 4"
- Operating Pressure: up to 300 PSI
- Microprocessor Control Panel
Daily Capacity Range:
25,200 to 155,700 GPD
(95 to 589 M³/day)
- Membrane Diameter: 8"
- Operating Pressure: up to 300 PSI
- Microprocessor Control Panel
Daily Capacity Range:
190,000 to 855,000 GPD
(719 to 3,236 M³/day)
- Membrane Diameter: 8"
- Operating Pressure: up to 300 PSI
- PLC Control Panel
Pure Aqua has over 20 years of experience as a global supplier of industrial and commercial nanofiltration systems for the removal of unwanted impurities from water. Our NF systems ensure the production of clean and potable water for any type of application in the water treatment industry. Check out our selection of nanofiltration systems for commercial establishments and industrial plants to meet your water treatment needs.
Nanofiltration (NF), in water treatment, “bridges” a gap between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. It is sometimes referred to as a loose or lower rejecting RO membrane. It could also be called a tight UF, as NF membrane pore size ranges from .01 to a little less than .001. Generally, an NF membrane system lets more salt pass than an RO membrane. In addition, an NF membrane element will produce the same quantity of product at 50 to 70% the applied pressure as an RO water treatment system.
There are applications where a 75% rate of salt rejection is preferable to 95 to 99%, especially when it is achieved using only half of the energy. Unlike with RO membrane elements, the NF offerings of the major membrane manufacturers are quite different in performance from company to company. With RO membrane elements, any model with less than 99.5% sodium chloride rejection, especially with seawater membranes, is considered inferior. In the case of NF, there is a “place” for any membrane with a NaCl rejection rate of 40%, or more. Nanofiltration has also been called a “softening” membrane as while its salt rejection may be 80% or less, hardness rejection will often remain well over 90%.
Other applications of nanofiltration include:
-
The removal of heavy metals from wastewater
-
The removal of pesticides from groundwater
-
Recycling of wastewater in laundries
-
Water softening
-
Nitrate removal
Questions & Answers
What is nanofiltration membrane?
Nanofiltration membranes are utilized for the filtration of water with low total dissolved solids (TDS) for the purposes of eradicating organic substances and softening water. Nanofiltration is usable in many water and wastewater treatment industries for the practical removal of ions and organic material. It has also been adopted as pretreatment to RO. Other than water purification, nanofiltration membranes are also used in the manufacturing production of food & beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
Difference between nanofiltration and reverse osmosis?
While nanofiltration and reverse osmosis systems have similar designs and operation uses, there are some notable differences between the two. The primary distinction is that nanofiltration is not as rigid as reverse osmosis. It functions with less feed water pressure and is incapable of removing single charge ions from the water as definitely as reverse osmosis membranes.
While up to 99% of chlorides and sodium are removed by reverse osmosis systems, nanofiltration membranes typically remove only 50% to 80%. This percentage relies on the type of material and manufacturing of the membrane. However, due to its effectiveness in removing multiple charge ions, nanofiltration is the preferred choice for removing hardness from water while not affecting the total dissolved solids content than would reverse osmosis.
Examples of Nanofiltration NF Applications:
| Application | Permeate | Concentrate | Benefits of NF |
| Whey / Whey Permeate | Salty wastewater | Desalted whey concentrate | Allows the recovery of lactose and whey protein concentrate with reduced salt content |
| Textile | Dyes | Water, salts, BOD, COD and color | NF is used to desalt dyes resulting in a higher value product |
| Caustic cleaning solutions | Caustic cleaning solution | BOD, COD, suspended solids, caustic cleaner | Allows caustic cleaning solution to be recycled resulting in reduced cleaning chemical costs |
| Recycle of acid solutions | Acid solution | BOD, COD, calcium, suspended solids, acidic water | Allows acid solution to be recycled resulting in reduced cleaning chemical costs |
| Water | Softened water | Hard water | Potable water production. Softened water reduces scaling on equipment and heat exchange surfaces |
| Antibiotics | Salty waste product | Desalted, concentrated Antibiotics | NF produces high value pharmaceutical products |
 ENGLISH
ENGLISH
 ESPAÑOL
ESPAÑOL العربية
العربية PORTUGUÉS
PORTUGUÉS FRANÇAIS
FRANÇAIS