As SAR levels increase, two instances occur: the soil becomes saline around the roots of a plant or the soil surface becomes less permeable. In both cases, plants suffer from water deprivation due to sodium interactions in the soil. Saline soil consists of abundant amounts of sodium in the soil that attracts water molecules taking away the water designated for the roots. Although the soil may seem moisturized on the surface, the soil surrounding the roots of the plant is filled with salt that is absorbing the water away from the plant.
Sodium hazard consists of salt buildup on the surface of the soil causing difficulty for the water to seep through to the roots of the plant. Therefore, water treatment systems are recommended to ensure that SAR levels are maintained and balanced to preserve the health of the soil in order to produce adequate products. This would occur through filtering out the particles and salts from the water source with none other than a reverse osmosis system.
[custom-specifications]
Sodium Adsorption Ratio refers to the ratio of sodium to calcium and magnesium in the soil due to their countering chemical effects. Maintaining the chemical composition of soil is a crucial component to the preservation and health of plants and crops. However, it can often be overlooked and not taken more seriously into consideration when efforts are made to ensure the sustainability of a plant or crop. The sodium can be slowly building up in the soil and one may not notice until their entire field seems to have gone through a drought.
Salinity and sodium are two issues that occur in terms of SAR. Measurements like total dissolved solids (TDS) and electric conductivity (EC) help indicate the hazardous issues that contribute to an increased sodium absorption ratio (SAR). Total dissolved solids (TDS) measures the amount of particles, contaminants, and salts in the water through parts per million (PPM). When TDS levels are high, it is indicative of an elevated number of salts which is associated with the level of SAR. As far as electrical conductivity, when the EC is low, the SAR is relatively low. When the EC levels are high (whether there are elevated amounts of sodium or not), the SAR level will be high. The issue with having high SAR levels is plant growth and survival.
[/custom-specifications]
[custom-features]
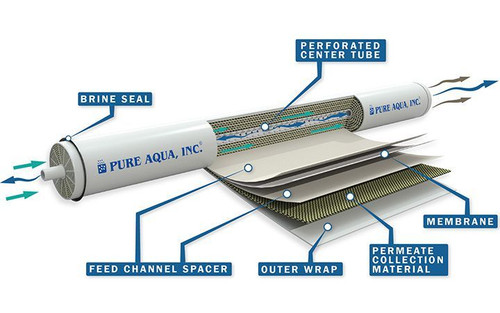
Reverse Osmosis System
Reverse Osmosis systems are rightfully known for their ability to purify water by filtering out almost all particles, TDS, and salts by 97%. The process of this water treatment includes a pressure driven water source that filters out majority of contaminants including sodium through a reverse osmosis membrane. This system is designed to prevent potential negative effects of water contamination for the application of the water. In this case, an RO system will ensure that the TDS levels remain low which will help maintain a balanced sodium absorption ratio level.
Related Projects:
- Commercial Reverse Osmosis for Irrigation 15,000 GPD - USA
- Industrial RO for Irrigation Use 72,000 GPD - USA
- Commercial Reverse Osmosis Kit RO 2X 7,500 GPD - USA
[/custom-features]
[custom-usage]
SAR Reduction Advantages:
- Increased product yield
- Healthy soil
- Lowers total dissolved solids (TDS)
- Balances electric conductivity (EC)
[/custom-usage]
[custom-documents]
[/custom-documents]
-
Terrific information
I understand how SAR reduction works now!
- Related Project1:
- https://pureaqua.com/industrial-ro-for-irrigation-sulfate-reduction-72000-gpd-usa/
- Related Project2:
- https://pureaqua.com/commercial-reverse-osmosis-kit-22000-gpd-ecuador/
- Related Project3:
- https://pureaqua.com/commercial-reverse-osmosis-for-irrigation-15000-gpd-usa/
- Related Project4:
- https://pureaqua.com/high-brackish-ro-plant-10000-gpd-usa/
 ENGLISH
ENGLISH
 ESPAÑOL
ESPAÑOL العربية
العربية PORTUGUÉS
PORTUGUÉS FRANÇAIS
FRANÇAIS